The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis is a method for the synthesis of pyrroles from α,β-unsaturated ketones and hydrazines. It was developed by Professors Derek Barton and Mark Zard in the 1980s and has since become a widely used strategy for the construction of substituted pyrrole rings.
The general reaction scheme for the Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis is as follows:
α,β-unsaturated ketone+Hydrazine→Pyrrole
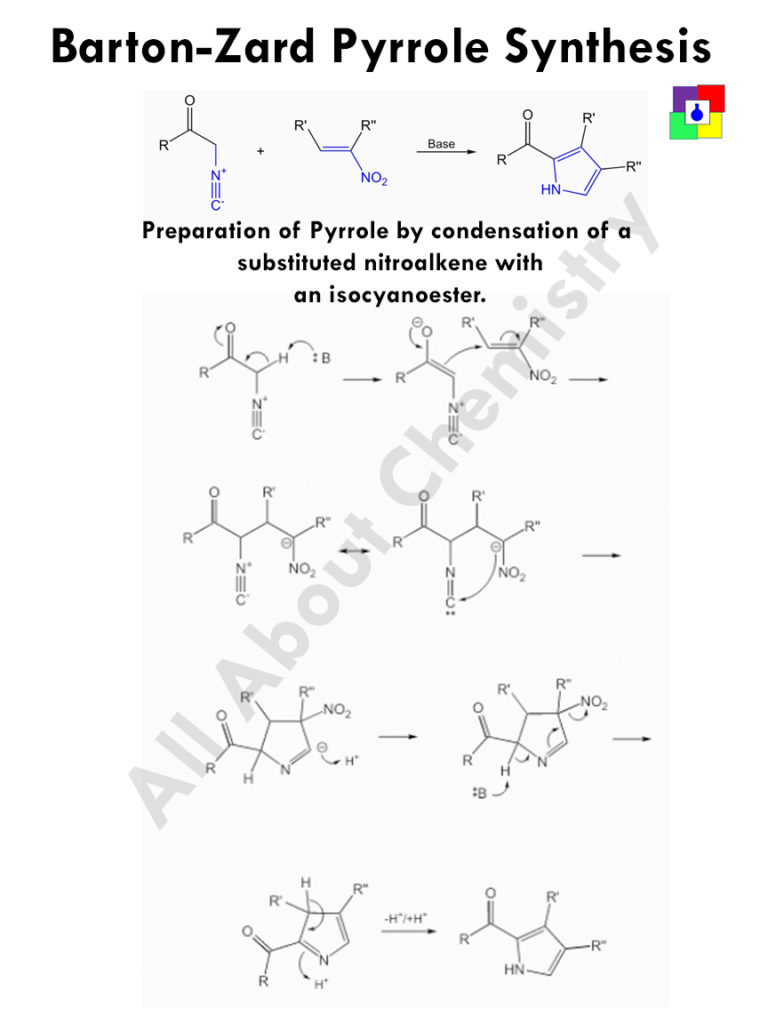
Barton-Zard Pyrrole Synthesis is the process of preparing substituted pyrrole by condensing substituted nitroalkenes with an isocyanoester.
- One alpha hydrogen is removed by the base to form a conjugate base.
- The conjugate base then add with the double bond opposite to the nitro site.
- The negative charge of the carbanion thus produced, combine with the Carbon atom of -CN group.
- After the ring closure, the negatively charged double bond accept proton to become neutral.
- From the other side of the nitrogen, one alpha hydrogen is removed by the base.
- This negative charge now gets delocalised, and ultimately leaves the nitro group from the molecule.
- Finally rearrangement of double bonds occur.
The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis involves several steps and intermediates, leading to the formation of pyrrole from an α,β-unsaturated ketone and hydrazine. Here’s a detailed mechanism:
- Condensation: The α,β-unsaturated ketone reacts with hydrazine to form a hydrazone intermediate. This step is facilitated by the presence of an acid catalyst such as acetic acid.
α,β-unsaturated ketone+Hydrazine→Hydrazone
- Tautomerization: The hydrazone undergoes tautomerization to form an azine intermediate. This step involves migration of a hydrogen atom from the hydrazine nitrogen to the adjacent carbon, resulting in the formation of a carbon-nitrogen double bond.
Hydrazone→Azine
- Cyclization: The azine intermediate undergoes intramolecular cyclization via nucleophilic attack of the nitrogen atom on the carbonyl carbon of the ketone moiety. This step forms a cyclic imine intermediate.
Azine→Cyclic Imine
- Tautomerization: The cyclic imine undergoes tautomerization to form an enamine intermediate. In this step, a proton from the nitrogen adjacent to the carbonyl group migrates to the carbonyl oxygen, resulting in the formation of a carbon-carbon double bond.
Cyclic Imine→Enamine
- Elimination: The enamine intermediate undergoes elimination of a molecule of ammonia (NH3NH3) to form the pyrrole ring. This step involves proton abstraction by a neighboring nitrogen atom, leading to the formation of the pyrrole ring and regeneration of the hydrazone.
Enamine→Pyrrole+NH3
The overall transformation involves the sequential condensation of the α,β-unsaturated ketone with hydrazine, followed by tautomerization, cyclization, and elimination steps to yield the pyrrole product. The mechanism proceeds under mild acidic conditions and often requires heating to facilitate the reaction. The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis offers an efficient and versatile method for the construction of substituted pyrrole derivatives in organic synthesis.
The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis has numerous applications in organic synthesis due to its efficiency and versatility in the construction of pyrrole rings. Some of the key applications include:
- Natural Product Synthesis: Pyrroles are structural motifs found in numerous natural products, including alkaloids, antibiotics, and biologically active compounds. The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis is utilized in the synthesis of these natural products and their analogs. By providing a practical method for the construction of pyrrole rings, this reaction enables access to diverse structural scaffolds for biological evaluation and drug discovery efforts.
- Medicinal Chemistry: Pyrroles exhibit a wide range of pharmacological activities, including antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and anticancer properties. The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis is employed in medicinal chemistry research for the synthesis of pyrrole-based pharmaceutical compounds. These compounds may serve as lead candidates for the development of new drugs targeting various diseases and medical conditions.
- Materials Science: Pyrrole-containing compounds are valuable building blocks in materials science and polymer chemistry. The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis is used to synthesize pyrrole monomers for the preparation of conducting polymers, such as polypyrrole, which exhibit electrical conductivity and have applications in electronics, sensors, and energy storage devices.
- Functional Molecule Synthesis: Pyrroles can be functionalized with various substituents to modulate their chemical and physical properties. The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis provides access to substituted pyrrole derivatives, which can be further elaborated through additional chemical transformations. These functionalized pyrroles serve as precursors for the synthesis of complex molecules with tailored properties for specific applications in organic synthesis and materials science.
- Pigment Synthesis: Pyrrole-containing compounds are utilized in the synthesis of pigments and dyes. The Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis can be employed to access pyrrole-based dyes and pigments for use in various applications, including textile dyeing, printing, and coloring of plastics and coatings.
Overall, the Barton-Zard pyrrole synthesis offers a valuable synthetic tool for the construction of pyrrole rings, enabling diverse applications in organic synthesis, medicinal chemistry, materials science, and pigment synthesis. Its efficiency, versatility, and applicability to a wide range of substrates make it a valuable method in the toolkit of synthetic chemists.








